Are you stepping into the world of CNC machining? The first thing you’ll hear about is G-code. It might seem like a lot at first, but really, it’s not too bad once you get the hang of it. G-code is basically how you talk to CNC machines. It tells them exactly how they should move, where they need to cut, and how fast to do it. So, whether you are using milling machines, lathes, or even 3D printers, knowing G-code for beginners is super important for proficiency!
What Exactly is G-Code
In short, G-code is a programming language. CNC machines use it to know what to do. If you write a G-code, it is a series of very detailed instructions, and these instructions guide the movements of the machine very carefully. Each line in the program tells the machine to do one specific thing. This could be anything from moving to a particular spot, turning on the spindle, or changing out the tools.
Think about it like this: G-code is the instruction manual for your CNC machine, which transforms raw materials into whatever you want. Without G-code, the machine is just a big paperweight because it would have zero clue of what it needs to do.
Why Beginners Should Learn G-Code
You might be thinking, Well, I can just use CAM software to make the G-code for me. And that’s true, but understanding the basics yourself is still really helpful. Here is why:
- Easier Troubleshooting: Let’s say your machine is not cutting right. If you know G-code, you can quickly figure out what is wrong and fix it.
- Custom Projects: Sometimes, the CAM software has limitations and won’t let you do special tasks. That’s when knowing how to write or adjust G-code manually can really save the day.
- Better Understanding of CNC Machining: When you learn G-code for beginners, you start to understand how the machine thinks. It is very important and enables you to do things more efficiently.
Common G-Code Commands
G-code for beginners has tons of commands, but don’t worry, start small with the most important stuff first. Here is a table that could help you get started:
| Command | What It Does |
|---|---|
| G00 | Moves the tool quickly to a specific spot |
| G01 | Moves the tool in a straight line |
| G02 | Creates a clockwise arc |
| G03 | Creates a counterclockwise arc |
| M03 | Turns the spindle on (clockwise) |
| M05 | Turns the spindle off |
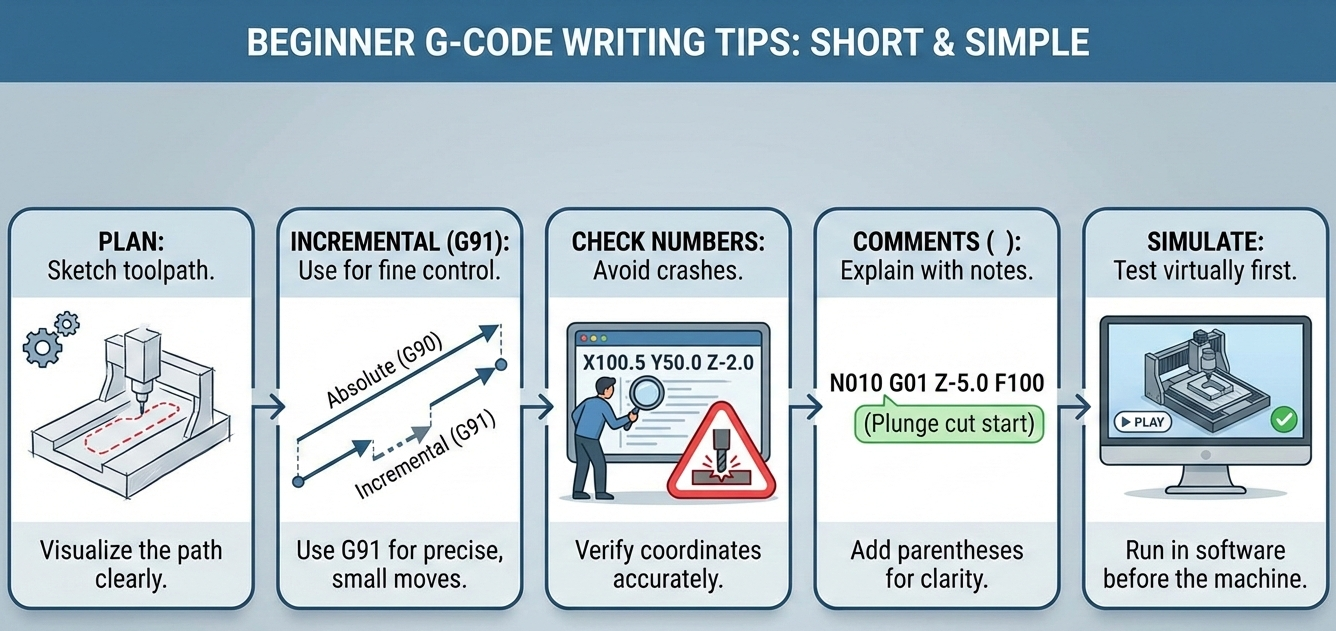
Some Tips for Writing G-Code
When you start writing G-code, you need to keep a couple of things in mind:
- Make a Plan: Always have a clear idea of the path you want the tool to follow.
- Use Incremental Movements: Sometimes, using incremental movements (G91) gives you finer control.
- Double-Check Your Numbers: Make sure your coordinates are correct to avoid crashing the machine.
- Add Comments: Use ( ) parentheses to add comments to your code, which makes it easier to understand later.
- Simulate Before Running: Before running the code on the real machine, test it in a simulator software.
Understanding Coordinates
One of the most important things to understand is how the coordinate system works. CNC machines operate in 3D space, defined by the X, Y, and Z axes. The G-code for beginners tells the machine where to move along these axes. Here’s a simple rundown:
- X-axis: This controls movement from left to right.
- Y-axis: This controls movement forward and backward.
- Z-axis: This controls movement up and down.
Also, there are two important types of positioning: absolute (G90) and incremental (G91). Absolute positioning means that all coordinates are based on a fixed point (the origin). Incremental positioning indicates that the coordinates are relative to the current position of the tool. It’s super important to know when to use each type to ensure accurate machining.
Feed Rates and Spindle Speeds
Another important part of G-code is controlling how fast the tool moves (feed rate) and how fast it spins (spindle speed). If you use the right settings, you will prevent the tool from wearing out too fast and improve the finish of your product. Here are the basics:
- F – This stands for feed rate, and it’s measured in mm/min (millimeters per minute).
- S -This stands for spindle speed, and it’s measured in RPM (revolutions per minute).
A common mistake is moving too fast or spinning the tool too quickly. Start slow and then increase little by little as you feel confident.
Here are some of the most common mistakes beginners make:
- Running code without simulating
- Forgetting to zero the machine
- Mixing up incremental and absolute
- Ignoring tool offsets
FAQs
1. How long will it take me to learn G-code?
If you are just learning the basics, you will be able to write programs in only a few weeks if you keep practicing. If you want to be a master, this will take months of doing things yourself.
2. Do I even need G-code if I’m using CAM software?
You can use CAM software that generates G-code for you. Knowing G-code is still helpful for fixing mistakes your softwares does, optimizing the program.
3. Can I practice G-code even if I don’t have a CNC machine?
Yes! You can download open-source G-code simulators online.
Contact Us!
📞 +91 99137 89065