In today’s fast-moving production world, staying ahead means knowing your stuff and understanding what others are doing. That’s where reverse engineering manufacturing comes in. It’s all about taking products apart to see how they work, what they’re made of, and how you might even make them better. So, let’s talk about what reverse engineering is, how it’s done, what tools are used, and why it’s such a big deal.
What is Reverse Engineering in Manufacturing
Reverse engineering in manufacturing means taking a product apart to figure out how it was designed, what materials were used, and how it works. Think of it as a puzzle – you look at all the pieces to understand how the whole thing was put together and how you can make it better.
In traditional production, the process starts with a plan and ends with a product. Reverse engineering flips that around: you start with a finished product and work backward to figure out the plan, what it’s supposed to do, and how it was made.
Why Manufacturers Use Reverse Engineering
Production companies use reverse engineering for various reasons.
- Making Products Better: By studying what your rivals are doing, you can spot what they’re good at and what they’re not so good at. This gives you ideas on improving your things.
- Cutting Costs: Sometimes, reverse engineering helps you find ways to make parts more affordably.
- Making Old Parts Again: Got some older machines that need parts, but no one has the designs anymore? Reverse engineering manufacturing can help you make those parts again.
- Keeping Things Consistent: Want to make sure your products are up to standard? Reverse engineering can help you review them and identify areas for improvement.
Reverse engineering is changing the game across all kinds of areas, from automotives and electronics to planes and everyday store-bought items.
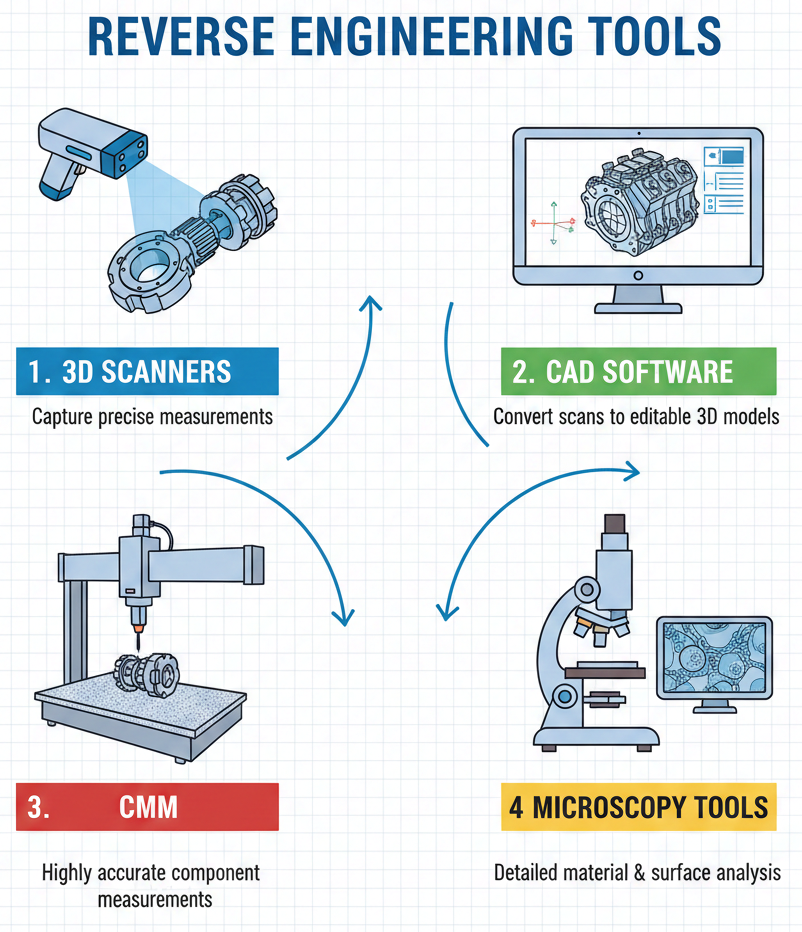
Tools for Reverse Engineering
The tools you need for reverse engineering manufacturing depend on the product’s complexity. Generally, here are some things that are commonly used:
- 3D Scanners: These take really accurate measurements of objects.
- CAD Software: This converts scanned objects into 3D models you can adjust on a computer.
- Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM): This gives super close measurements for complex pieces.
- Microscopy Tools: When you need to analyze materials closely, these are amazing. If you need to examine the surface microstructure of a part, these microscopes are very helpful.
Here’s a table showing some tools and their purposes:
| Tool | Purpose | Example Industries |
|---|---|---|
| 3D Scanner | Get digital measurements of objects | Cars, Planes |
| CAD Software | Make 3D models from scan data | Electronics, Home Goods |
| CMM | Measure complex parts with high accuracy | Production, Tool Making |
| Microscope | Analyze material surfaces and microstructure | Material Science, Research |
These tools make it easier to copy, modify, or improve existing content without starting from scratch.
The Reverse Engineering Process
Reverse engineering usually follows these steps:
- Collect Info: Get all the info about the product -measurements, what it’s made of, how it works, etc.
- Take It Apart: Carefully disassemble the product to study each piece.
- Analyze and Write It Down: Study the materials, the design, and how they were put together.
- Make a 3D Model: Use CAD to make digital models of the product.
- Test and Improve: Build some examples to see whether the design works and where you can improve it.
This way of doing things keeps it accurate but also reduces mistakes, which is super important when dealing with tricky production parts.
Benefits of Reverse Engineering
Here are some of the perks of using reverse engineering in production:
- Faster Product Creation: Understanding how other products work can accelerate the design of new products.
- Stay Ahead: Analyzing what your rivals are doing can spark new ideas.
- Save Money: Reduces the need to make multiple tries when designing something.
- Keep Knowledge Alive: Helps you document the designs of older or discontinued products.
- Customization: Allows you to adjust products to meet specific needs or customers.
In easy words, reverse engineering doesn’t just copy – it improves. You can make things that work better, cost less, and stay top-of-the-line.
FAQs
Q1: Can I legally do reverse engineering in manufacturing?
Yes, if you’re doing it to learn, repair, or better something. But copying things that are patented may violate intellectual property laws.
Q2: Is it possible to cut production costs by doing reverse engineering?
Yes, by studying other products, you can find ways to use them and make things cost-effective. Plus, it can help reduce waste and improve things.
Q3: Which industries benefit most from doing reverse engineering?
Industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, consumer goods, and medical devices benefit greatly from improving their parts and designs.
Contact Us!
📞 +91 99137 89065
